This article is going to dive into what foods improve gut health and why it aids in digestion, boosts immunity, and supports overall health.
Incorporating the proper ratio of probiotics, prebiotics, and fiber-loaded foods into your daily regimen can enhance gut health, improve digestive health and gut-related issues, and improve digestive and overall health holistically.
Key Points & Best Food For Gut Health List
| Food | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Contains probiotics that improve gut bacteria balance. |
| Kefir | Fermented drink rich in probiotics and nutrients for digestion. |
| Sauerkraut | Fermented cabbage that supports healthy gut microbiota. |
| Kimchi | Spicy fermented vegetable dish with probiotics and fiber. |
| Kombucha | Fermented tea that boosts beneficial gut bacteria. |
| Whole Grains | High in fiber, which feeds good gut bacteria. |
| Garlic | Acts as a prebiotic, promoting growth of healthy gut bacteria. |
| Bananas | Contain fiber and resistant starch that nourish gut bacteria. |
| Ginger | Supports digestion and reduces inflammation in the gut. |
| Apples | High in fiber and polyphenols, promoting healthy gut microbiome. |
10 Best Food For Gut Health
1. Yogurt
Yogurt is a kind of dairy food that goes through fermentation. It is filled with probiotics or good bacteria that help intestinal microbiota.
Eating yogurt can improve digestion, boost immunity, and alleviate bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
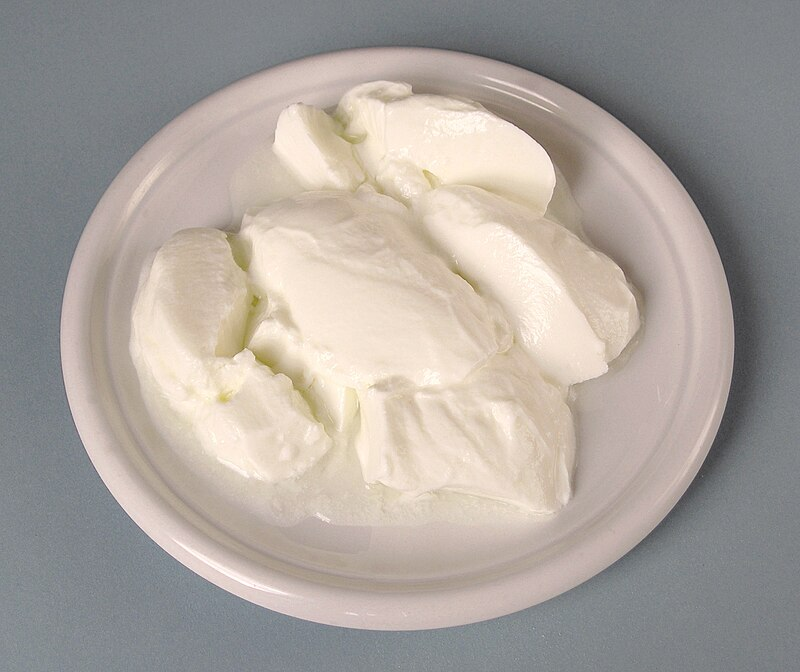

Yogurt is a good source of protein and calcium. For enhanced health benefits, consume yogurt that is plain and unsweetened to avoid extra sugars that can negatively impact gut bacteria.
Yogurt can be eaten as is, added to cereals and fruits, or blended with smoothies. This food is easy to incorporate into the diet and is beneficial for gut health as well.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fermented dairy product |
| Key Benefit | Rich in probiotics that improve gut bacteria balance |
| Nutrients | Protein, calcium, vitamin B12 |
| Digestive Aid | Helps with constipation, bloating, and diarrhea |
| Consumption Tips | Best consumed plain or in smoothies; avoid added sugar |
| Frequency | Daily for maximum gut benefits |
2. Kefir
Kefir is a fermented probiotic drink which is more nutritious than yogurt because it contains probiotics, assists gut health, aids in digestion, reduces inflammation, and helps in immune support.
Kefir is a rich source of Protein, calcium, vitamin 312, and magnesium. Moreover, unlike yogurt, kefir is a bit tangy and is more drinkable because of its thinner texture.

Regular intake of kefir helps in symptom reduction of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and nutrient absorption. Kefir contains bioactive compounds which coupled with probiotics makes kefir a gut super food.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fermented milk drink |
| Key Benefit | Contains diverse probiotics for healthy gut microbiome |
| Nutrients | Protein, calcium, magnesium, vitamin B12 |
| Digestive Aid | Improves digestion and nutrient absorption |
| Consumption Tips | Can be drunk as is or added to smoothies |
| Frequency | Daily consumption recommended |
3. Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is lactic acid fermented shredded cabbage which is preserved with salt. Sauerkraut is a source of probiotics with a rich fiber content.
Sauerkraut also contains vitamin C and vitamin K which all aids in digestion, boosts immune system functionality, and helps with gut health.
Nutritional fermentation helps the sauerkraut which promotes gut bacteria. Eating sauerkraut regularly promotes mental health and also aids in digestion and elimination of bowel sluggishness.
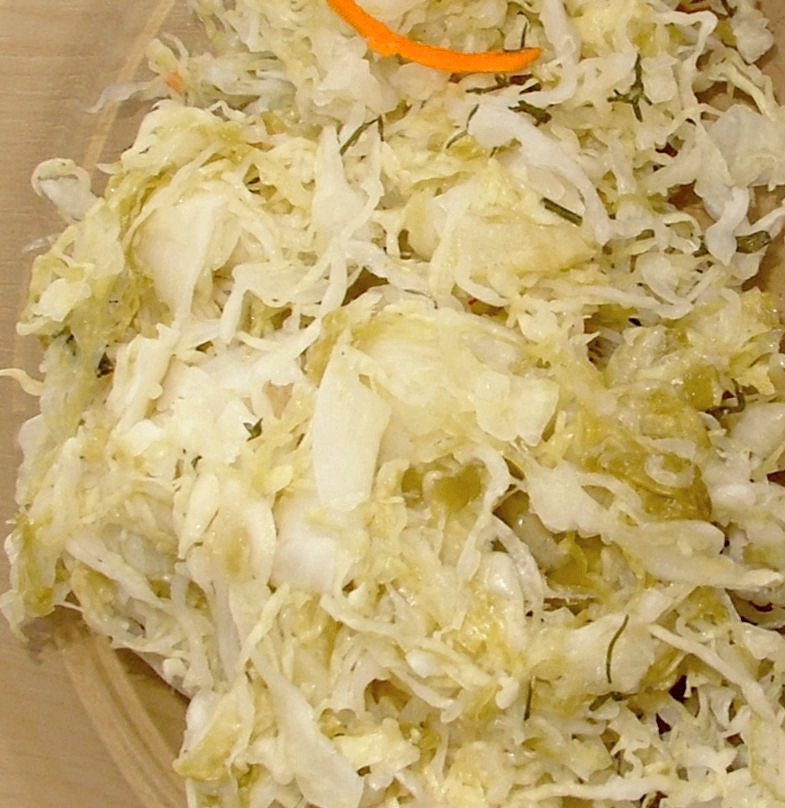

It can be consumed in salads, sandwiches, and eaten alone. The sauerkraut which is fermented and unpasteurized serves as the best source of probiotics.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fermented cabbage |
| Key Benefit | Rich in probiotics and fiber |
| Nutrients | Vitamin C, vitamin K, antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Supports bowel regularity and gut microbiota |
| Consumption Tips | Eat raw for maximum probiotics; can be a salad topping or side dish |
| Frequency | Several times a week |
4. Kimchi
Considered a staple of Korean cuisine, Kimchi consists of fermented vegetables, usually of cabbage and radish, mixed with garlic, chili, and other spices.
This dish is full of probiotics, fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, all of which helps improve gut microbiota, digestion, and immune systems.
The fermentation process produces lactic acid which aids healthy intestinal bacteria, all which help absorb more nutrients.
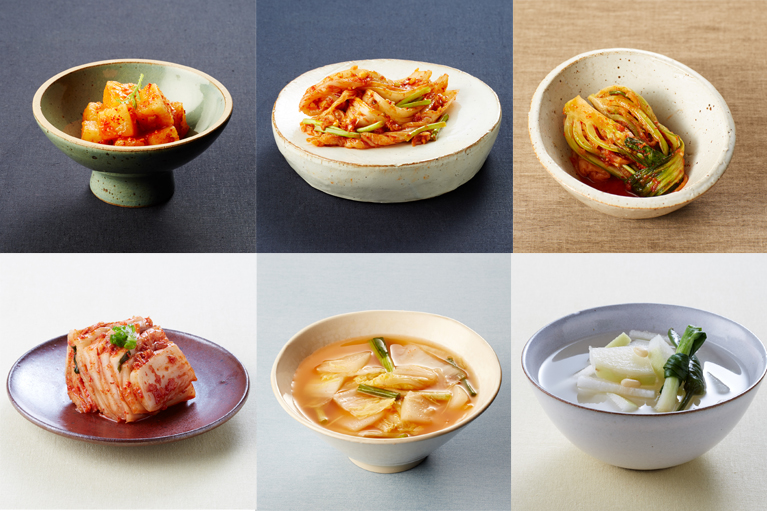

The inflammation that can occur is reduced with Kimchi’s bioactive compounds, and it has potential to improve metabolic function.
This dish accompanies soups and rice, and can be eaten on its own as a side. Regularly eating Kimchi can help improve digestion, while also boosting immune function and heart health.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fermented vegetables (cabbage, radish) |
| Key Benefit | Boosts probiotics and gut microbiome diversity |
| Nutrients | Fiber, vitamins A, C, K, antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Improves digestion and reduces gut inflammation |
| Consumption Tips | Can be eaten as a side dish, in soups, or with rice |
| Frequency | Several times a week |
5. Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea made with probiotics, organic acids, and antioxidants that help improve and support gut health and digestion.
The bacteria in probiotics help foster a healthy gut microbiome which helps cut down bloating and improve nutrient absorption.
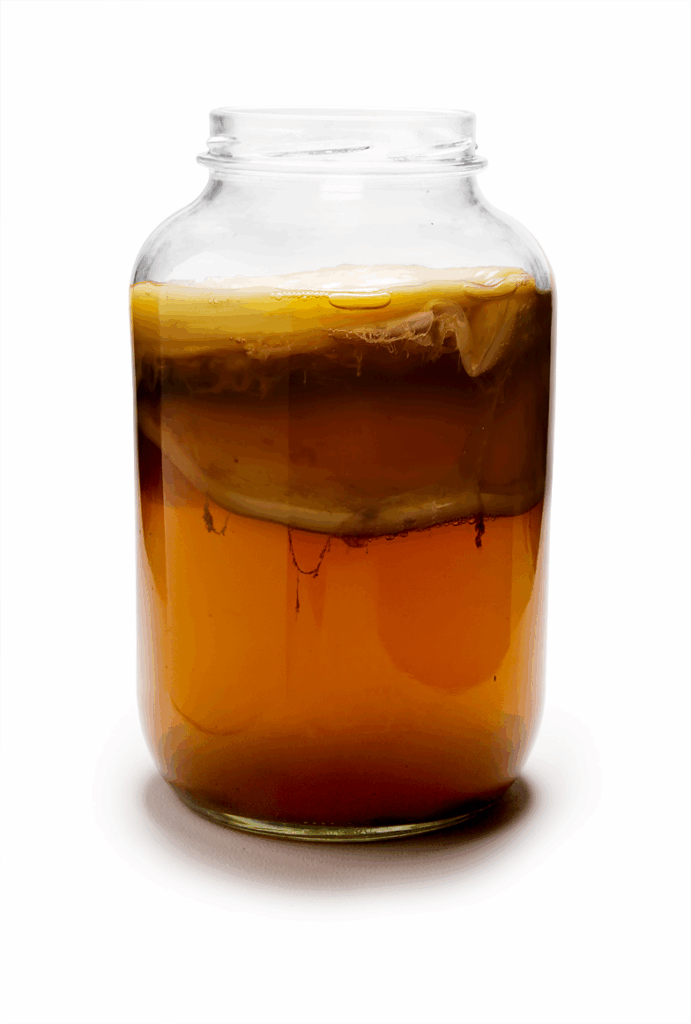

The tea also has polyphenols which function as antioxidants that support the gut and liver. It may also improve energy while boosting immunity and aiding in detox.
Kombucha has a slight tartness and fizziness, with many different flavors to choose from. It’s best to drink in small amounts for gut-friendly benefits
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fermented tea |
| Key Benefit | Contains probiotics and antioxidants |
| Nutrients | Organic acids, polyphenols, small amounts of B vitamins |
| Digestive Aid | Supports healthy gut bacteria and detoxification |
| Consumption Tips | Drink in small amounts daily; flavored varieties available |
| Frequency | Daily or several times a week |
6. Whole Grains
Brown rice, oats, quinoa, and barley are whole grains. Whole grains are sources of fiber, especially insoluble and soluble fiber. They help nourish the good bacteria in the gut.
Fiber helps with proper bowel movements, prevents constipation, and maintains gut health. Whole grains are also sources of important digestive health vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and antioxidants.
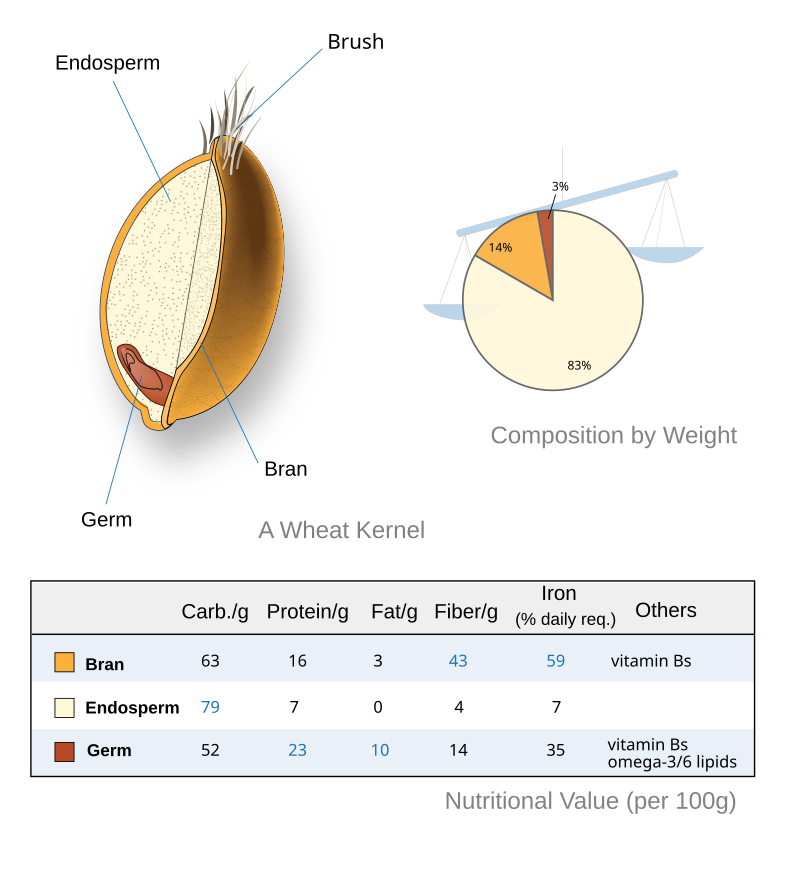
Whole grains have been shown to help with inflammation of the gut, lower the risk of colon cancer, and help with issues like metabolic disorders.
Whole grains also make great additions to salads, cereals, soups, and many side dishes. Eating whole grains on a daily basis will improve gut health, along with overall health.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Oats, brown rice, quinoa, barley |
| Key Benefit | High in fiber that feeds good gut bacteria |
| Nutrients | B vitamins, iron, magnesium, antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Promotes bowel regularity and healthy microbiome |
| Consumption Tips | Use in breakfast, salads, soups, or side dishes |
| Frequency | Daily consumption recommended |
7. Garlic
Garlic is rich in prebiotic fiber which is food for many of the beneficial bacteria in gut and helps to starve the bad bacteria. Inulin and fructooligosaccharides are important compounds in gut health. They improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
They are also antioxidants and reduce inflammation, which helps with gut lining health. Garlic is thought to minimize bloating and improve balance of the intestinal flora.
Garlic is extraordinary and well-loved for many reasons. It can be consumed raw, cooked, or roasted and is commonly found in sauces, soups, and stir fries.
Garlic is easy to mix in a variety of dishes and adds an abundance of beneficial bacteria to the gut which makes digestion easier, supporting overall gut health.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Natural prebiotic food |
| Key Benefit | Promotes growth of beneficial gut bacteria |
| Nutrients | Vitamins B6, C; manganese; antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Improves gut microbiome balance and digestion |
| Consumption Tips | Can be eaten raw, roasted, or in meals |
| Frequency | Daily or several times a week |
8. Bananas
Beneficial gut bacteria are fed with dietary fiber in the form of resistant starch that bananas provide.
They help regulate bowel movements and are important in preventing the constipation which plagues so many people in today’s world.
Bananas are also a source of vitamin C and vitamin B6 as well as potassium and a variety of antioxidants which contribute to the functioning of the gut and overall metabolic health.

Eating bananas may help to reduce inflammation in the gut, facilitate the absorption of various nutrients, and improve the gut microbiome as well.
Since bananas are sweet and soft, they can be added to smoothies, oatmeal, and even be enjoyed on their own or baked.
Bananas are also a very convenient and affordable fruit which makes them very accessible as a real go to for people looking to support their gut health.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fruit |
| Key Benefit | Rich in prebiotic fiber and resistant starch |
| Nutrients | Vitamins C, B6, potassium, antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Supports bowel regularity and healthy gut bacteria |
| Consumption Tips | Eat raw, in smoothies, oatmeal, or baked goods |
| Frequency | Daily consumption recommended |
9. Ginger
Like a number of other natural antidotes, ginger has been prescribed for digestive issues for its anti inflammatory and anti oxidant traits.
It also stimulates the production of digestive enzymes, improves the absorption of nutrients while also bloating, and decreases nausea or discomfort.
Ginger can also improve gut motility and help in the balance of gut microbiota which is vital for overall health.
The inflammation of the gut can be aided through regular consumption which in turn improves digestive health.
It can be also taken in a form of tea, added to smoothies, or fresh ginger can be added to other cooled or cooked dishes.
Other compounds in ginger, particularly gingerol, along with its bioactive compounds, make ginger very effective for gut health and overall well-being.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Root spice |
| Key Benefit | Reduces gut inflammation and supports digestion |
| Nutrients | Gingerol (bioactive compound), antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Relieves nausea, bloating, and improves nutrient absorption |
| Consumption Tips | Can be used fresh, in teas, smoothies, or cooking |
| Frequency | Daily or several times a week |
10. Apples
In terms of diet apples are good for you because they are rich in fiber. Apples are also a good source of pectin, which is a prebiotic that feeds the good bacteria in the gut.
Apples are bound to aid digestion, regulate bowel movement, and enhance the gut’s microbiome.
Apples enhance gut health and reduce gut inflammation because they are rich in vitamins, polyphenols, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds.

Eating apples on a regular basis helps reduce the chances of developing digestive system illnesses as well as stimulates the metabolic function.
Apples can be eaten plain, in salads, blended into smoothies, or used in baking. In addition to their sweetness that makes them versatile, apples are also extremely healthy for the gut.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Fruit |
| Key Benefit | High in fiber and polyphenols; promotes healthy gut bacteria |
| Nutrients | Vitamins C, potassium, antioxidants |
| Digestive Aid | Supports bowel regularity and overall gut microbiome |
| Consumption Tips | Eat raw, in salads, smoothies, or baked dishes |
| Frequency | Daily consumption recommended |
Conclusion
In conclusion, a person enjoys many gastral, immune system, and overall body gains from keen gut maintenance.
Including yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha, as well as whole grains, garlic, bananas, ginger, and apples provides powerful probiotics, prebiotics, fiber, and antioxidants working in harmony.
Consistently incorporating these gut-friendly foods and nutrients encourages gut microbiome balance; improves inflammation and digestion; and maintains digestive and overall gut health for many years to come.
FAQ
What are the best foods for gut health?
Foods rich in probiotics, prebiotics, fiber, and antioxidants, like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha, whole grains, garlic, bananas, ginger, and apples.
Why are probiotics important?
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that improve gut microbiome balance, digestion, and immunity.
What are prebiotics?
Prebiotics are fibers that feed good gut bacteria, promoting a healthy digestive system.
How does yogurt benefit the gut?
It provides live probiotics that enhance digestion, reduce bloating, and support healthy bacteria growth.
Can fermented foods improve digestion?
Yes, foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir support beneficial gut bacteria and reduce digestive issues.

